Currently, there are two scenarios where conductive bonding is used in the field of flow batteries:
Scene 1:
Currently, the flow channel structure on the bipolar plate of a flow battery is formed by placing a flow channel plate, which is made through die-cutting, wire-cutting, or other molding methods, onto the bipolar plate. It is then tightly attached to the bipolar plate through structural fastening or adhesive coating in the later stage. This method has several issues:
1. Insecure, the flow channel plate may be displaced due to various factors such as the movement of the fuel cell stack and long-term erosion by the electrolyte;
2. The glue used for dispensing or coating requires a certain pressure and time for surface drying and curing, thus the operation takes a long time, and pressing is required. The operation is cumbersome, leading to a long production cycle;
3. The glue used for dispensing and coating is generally not resistant to long-term acid-base and electrochemical corrosion;
4. Due to the relatively high internal resistance of conductive adhesive, local dispensing or coating is chosen. There will be height differences in the positions where no adhesive is applied, which prevents the flow channel plate on the bipolar plate from fitting tightly with the bipolar plate, resulting in high contact resistance;
5. The glue used for dispensing and coating is insulating. Of course, conductive glue can also be made by adding conductive agents to it. However, in order to resist acid-base and electrochemical corrosion, the conductive materials in the conductive agents are mostly high-surface-area nanoscale carbon materials, and their solid content is inherently low. Therefore, the conductivity of conductive glue is also relatively low. If the proportion of conductive materials is increased, the resin content will be relatively reduced, and the adhesion will decrease. Therefore, the conductivity of conductive glue is relatively poor.
Scene 2:
The electrode materials for zinc-bromine flow batteries primarily consist of various carbon material electrodes, such as porous carbon, graphite electrode cloth, or graphite electrode felt. Typically, the process involves hot-pressing the surface of a conductive plastic bipolar plate to melt it, and then adhering the carbon material electrode onto it. The advantage of this process is that the adhesion is strong. However, there are also issues, with the main problem being:
1. High-temperature hot pressing can damage the mechanical structure of electrode materials;
2. Under high temperatures, conductive plastic bipolar plates will undergo certain material volatilization, which, when adhering to carbon material electrodes, can cause damage to the active functional groups of the carbon material electrodes, thereby affecting performance.
In response to the aforementioned issues, the conductive hot-melt adhesive film prepared by our company possesses the following characteristics:
1. The material is primarily composed of thermoplastic resin, which exhibits excellent resistance to acid and alkali corrosion as well as electrochemical corrosion;
2. It has a lower hot-melt temperature and shorter hot-melt bonding time, making it very suitable for mass production;
3. Excellent adhesion strength, allowing for full coverage bonding on the entire surface, leaving no dead zones, and achieving overall adhesion;
4. With excellent conductivity, the conductivity is ≥15S/cm, which is higher than that of most conductive plastic bipolar plates, and it has a good effect on reducing contact resistance.
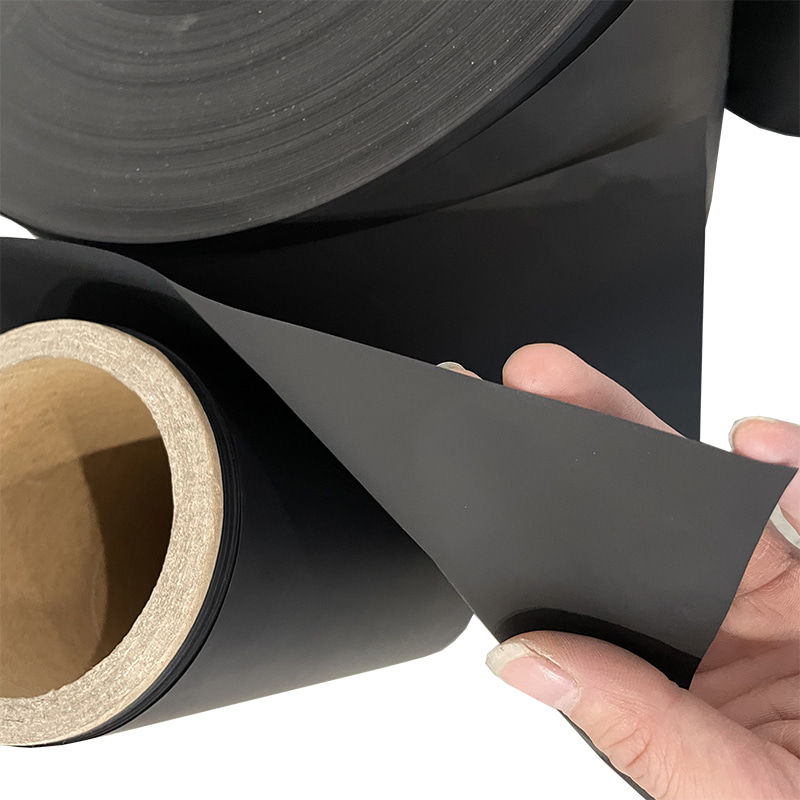
The product is packaged in a roll, easy to cut. It contains no solvents, does not evaporate, has no odor, and poses no environmental pollution concerns.
Conductive adhesive film
|
Carbon content |
Resistance value (Square resistance) |
Specific conductance |
Thickness |
Hot melt temperature |
Hot-pressing time |
|
≥30% |
≤100Ω |
≥15S/cm |
0.05-0.2mm |
≥70℃ |
≥30s |
Special note:
1. This conductive adhesive film is resistant to corrosion by various electrolyte systems such as all-vanadium,iron-chromium,zinc-bromine,etc.,and is also resistant to electrochemical corrosion;
2. In all-vanadium,iron-chromium and other systems,it can firmly bond bipolar plates and flow field plates to make bipolar plates with flow channels;
3. In zinc-bromine flow batteries,it can bond bipolar plates and electrodes (electrode cloth and electrode felt) together to make integrated electrodes.





 English
English  中文简体
中文简体